
WHAT IS CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME?
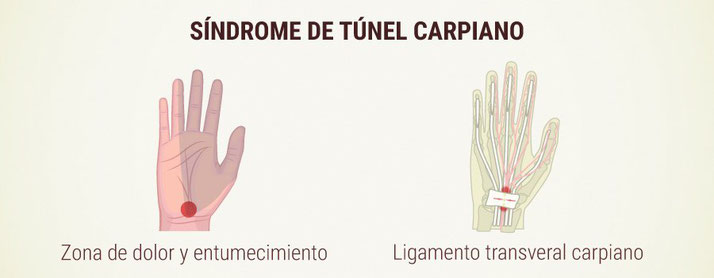
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a painful condition that affects the wrist. Specifically, it is caused by a pinched median nerve (one of the largest nerves in the hand). This syndrome is a recurring problem that tends to worsen over time, which means it's important to diagnose and treat it as soon as possible.
Over time, continued pressure on the median nerve can severely damage it. This damage is permanent and leads to worsening and more intense symptoms.
The carpal tunnel passes through the wrist and acts as a small passageway, protecting the median nerve as it passes from the hand to the arm and extends to the neck. The median nerve is one of the main nerves in the hand; it controls sensation in the fingers, as well as the muscles surrounding the thumb.
CTS occurs when the carpal tunnel compresses the median nerve. This can occur when the carpal tunnel narrows, or when a special tissue around the flexor tendons in the hand becomes inflamed. This inflammation can compress the carpal tunnel and put pressure on the median nerve.
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME?
External pressure compressing the median nerve causes a variety of symptoms. The severity of these symptoms tends to increase over time. If left untreated, carpal tunnel syndrome could cause permanent damage to the median nerve, which would only increase the severity of symptoms.
Some of the main symptoms of CTS are:
- Pain
- Numbness
- Tingle
- Weakness in the hand
- Cramp-like sensations running through the fingers
- Pain and cramps moving up the arm toward the shoulder
WHAT CAUSES CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME?
Research suggests that CTS is more common in older women. Several factors may increase the risk of developing this condition, including:
- Genetics: Physical traits, such as a smaller wrist or a narrower carpal tunnel, may increase a person's risk of developing CTS. These physical traits are likely passed down from one generation to the next.
- Hand movements and flexions: Performing repetitive hand movements, or activities that require extreme flexion of the wrists, hands, and fingers, could aggravate the wrist tendons and cause inflammation, which ultimately affects the median nerve.
- Arthritis: Inflammation of the joints in the hand and wrist may affect the carpal tunnel.
HOW IS CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME USUALLY TREATED?
Treatment for CTS begins with a medical exam. Your doctor will make a diagnosis based on your symptoms and a physical exam, which includes tapping, bending, and pressing various parts of your hand. Your doctor will also test your hand sensation and, in some cases, perform electrophysiological testing and medical imaging (such as ultrasound, MRI, and X-ray) to better identify the cause of your symptoms.
Once diagnosed, treatment varies depending on the severity of symptoms and the level of progression of the condition. When detected early, CTS symptoms can usually be treated with non-surgical methods, including:
- Wrist splints and orthoses: These keep the wrist in a neutral position and minimize pressure on the carpal tunnel.
- NSAID treatment: NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) are safe and well-tolerated, and can help relieve the pain and inflammation caused by this condition.
- Steroid injections: Corticosteroids are powerful anti-inflammatory agents that can help treat carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Exercises: Some doctors have their patients perform specific exercises designed to relieve symptoms and pressure around the median nerve.
- Lifestyle changes: Your doctor will help you identify activities that put additional pressure on the carpal tunnel and worsen your symptoms. This could affect your job, exercise routine, or even hobbies that require you to flex or straighten your hand and wrist frequently or for long periods of time.
CTS can also be treated surgically. These procedures, known as carpal tunnel release, enlarge the tunnel to relieve pressure surrounding the median nerve. The need for this surgery depends on the severity of the symptoms.
Could CBD help with carpal tunnel syndrome?
Since the main symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome are pain and inflammation, cannabis is an attractive option. Although conventional medications, such as NSAIDs and steroids, can effectively relieve carpal tunnel symptoms, incorrect or continuous use of these medications can lead to side effects.
NSAIDs, for example, can cause side effects such as gastrointestinal bleeding, heartburn, headaches, dizziness, liver and kidney problems, and high blood pressure, among others. Studies show that in the U.S., approximately 100,000 people are hospitalized each year for gastrointestinal problems related to NSAIDs alone. This increases the interest in seeking alternatives.
Over the past decade, several studies have demonstrated the anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of various cannabis components. In 2013, for example, researchers at Tongji University School of Medicine found that CBD[1] could significantly reduce inflammation in an animal-based study of pancreatitis.
In 2012, a study published in the European Journal of Pharmacology suggested that CBD might decrease inflammation[2] in rats with acute lung injuries. In 2011, researchers at the University of Naples Federico II found that CBD also appears to reduce chronic inflammation[3] in the gut. Other studies show how CBD might help reduce inflammation caused by arthritis[4] and IBS[5].
That said, more research is needed, so it's still unclear how effective cannabis may be in helping with carpal tunnel syndrome. Specific research on the condition and its relationship to cannabis is needed. Still, current research in this area is promising, although not yet definitive.
External Sources
Anti-inflammatory Role of Cannabidiol and O-1602 in Cerulein-Induced Acute Pancreatitis in Mice - PubMed https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Cannabidiol, a Non-Psychotropic Plant-Derived Cannabinoid, Decreases Inflammation in a Murine Model of Acute Lung Injury: Role for the Adenosine A(2A) Receptor - PubMed https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Cannabidiol Reduces Intestinal Inflammation Through the Control of Neuroimmune Axis - PubMed https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Preliminary Assessment of the Efficacy, Tolerability and Safety of a Cannabis-Based Medicine (Sativex) in the Treatment of Pain Caused by Rheumatoid Arthritis - PubMed https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Cannabidiol in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: A Brief Overview - PubMed https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
PRONAPRESA
"Because prevention is better than cure"





















































